VPD controls how much water the plant loses, which controls cooling, nutrient uptake, stomatal behaviour, and...
-
Bio Nutrientes
add remove
-
Nutrientes minerales
add remove
- Accesorios
-
Cómo hacerlo
add remove
- P.F.
- Blog
Buscar en blog
Categorías de blogs
Últimas entradas del blog

Extra mineral aerated compost tea (calcium and trace element)

How to make simple compost tea !

How to use autopot with Greenhouse Feeding mineral line

Autopot + GHF Bioline
Entradas de blog populares




Entradas de blog destacadas




What is VPD ?
What is VPD (Vapor Pressure Deficit)?
VPD is a measure of how the air is retaining water.
-
Warm air can hold a lot of moisture
-
Cold air holds less
-
If the air has less moisture than it can hold, it “pulls” water from plants
So:
-
Low VPD = air is humid → plants lose less water
-
High VPD = air is dry → plants lose more water
It is like a sponge:
-
A sponge that’s already wet can’t absorb much (low VPD)
-
A dry sponge absorbs water fast (high VPD)
Plants feel the same way about the air around them!
Why does it matter?
Because VPD controls how much a plant transpires.
-
If VPD is too low → plant can’t transpire → slow growth, wet leaves, mold risk
-
If VPD is too high → plant transpired too fast → stress, drooping, nutrient burn
So growers use VPD charts to keep plants in the “comfort zone.”
HOW VPD AFFECT PLANTS ?
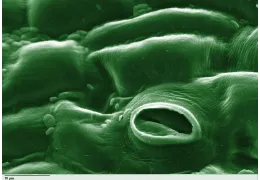
Stomata (like the picture of the post)
Plants have small openings on their leaves called stomata.
These open and close to regulate:
-
Water loss
-
CO₂ intake (for photosynthesis)
-
Cooling
Low VPD (air is humid):
-
Air is already full of moisture
-
Plant doesn’t need to lose much water
-
Stomata stay open
→ Good CO₂ exchange
→ Good photosynthesis
→ But risk of mold and slow transpiration
High VPD (air is dry):
-
Air is “thirsty”
-
Plant loses water too fast
-
Stomata close to prevent dehydration
→ Less CO₂
→ Slower photosynthesis
→ Stress, drooping, burnt tips
Nutrient Uptake
Water flow through the plant pulls nutrients from the roots upward.
-
Good VPD → steady transpiration → steady nutrient movement
-
Low VPD → water flows too slowly → nutrient deficiencies
-
High VPD → water moves too fast → nutrient burn (tips turn brown)
An incorrect VPD will lead to nutrient problems, that's why it is important to control your climat.
This is the first parameter to check begore starting growing ! Always make sure you can adjust the temperature and humidity level.
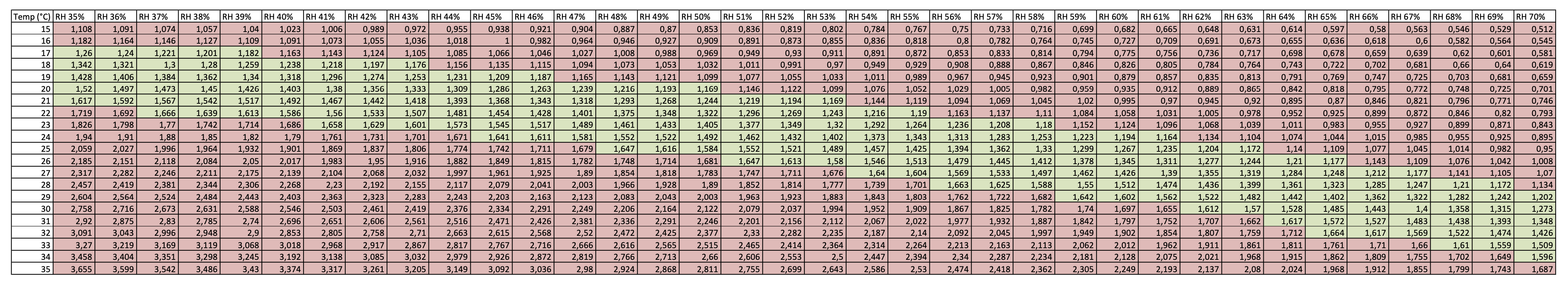
You can find VPD table here:
VEGETATIVE - EARLY FLOWER- VPD 0.8-1.2 KPA
When your plants are entering vigorous growth in late veg and early flower, they have more leaves and roots, so are able to take up more water and nutrients with this higher transpiration setting range.
LATE FLOWER – VPD 1.2-1.6 KPA
When your plants have stopped vegetative growth and are maturing in the flowering stage, they have a well established root system and leafy canopy to cope with a higher rate of transpiration. The increased water uptake is helpful at this setting range and the drier environment helps prevent pathogens.
VPD table for vegetative - early flower part:
VPD table for the flowering part:


Deja un comentario
Inicia sesión para publicar comentarios